Today managing corporate risks has become a crucial factor for success. As companies navigate through complex environments filled with uncertainties, enterprise risk management (ERM) emerges as a vital strategy to minimize financial losses and enhance reputation. ERM is not just a defensive measure; it’s a proactive approach that helps organizations grasp opportunities while safeguarding their assets.
This article delves into the world of ERM, explaining what it is, how to implement it effectively, the benefits it offers, and the tools that can aid in managing enterprise risks. Let’s explore how ERM can transform your organization’s risk management strategy and propel it towards success.
What is enterprise risk management? Understanding the Core Aspects and Components
In a business environment, enterprise risk management (ERM) is a systematic and comprehensive approach to managing risks across all aspects of a business, from operational to strategic. Its primary goal is to prevent losses and maximize value for shareholders and stakeholders, including employees, customers, and partners. ERM definition involves identifying, assessing, monitoring, and managing risks that could impact the achievement of strategic objectives. Providing a complete picture of risks, ERM empowers companies to make informed decisions about risk management.
ERM encompasses various types of risks, including financial, operational, reputational, strategic, and technological risks. This holistic view ensures that organizations can manage risks effectively within a unified strategy.
👉What is meant by enterprise risk management? Enterprise risk management definition includes a structured, organization-wide approach to identifying, assessing, managing, and monitoring risks that could affect an enterprise’s ability to achieve its objectives. It considers all types of risks—strategic, operational, financial, compliance, and reputational—ensuring a holistic view of risk management. ERM helps businesses proactively address uncertainties, improve decision-making, and create long-term value by integrating risk management into corporate strategy and day-to-day operations.
Explore Our Enterprise Use Cases
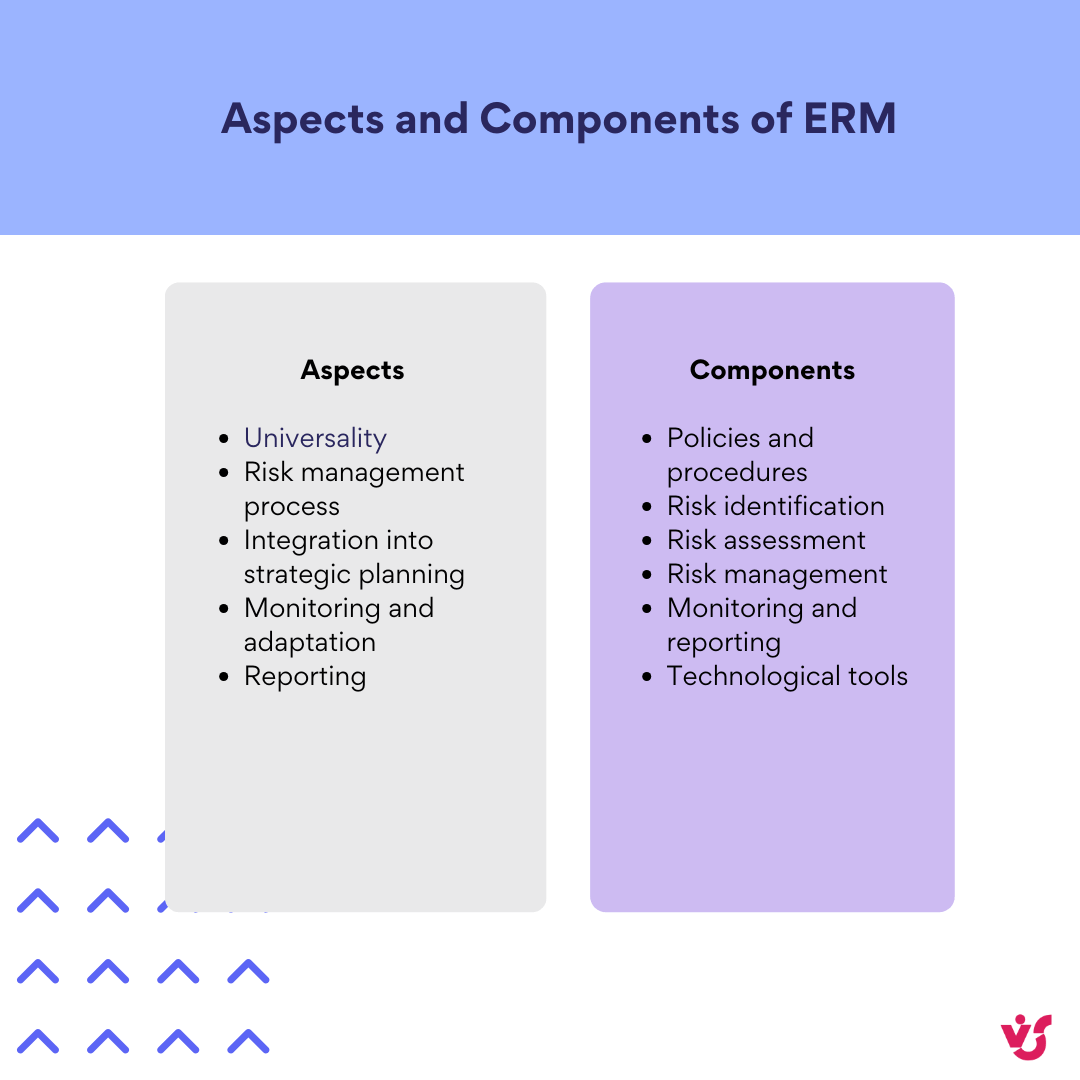
Core aspects of ERM
- Universality: ERM covers all types of risks, including financial, operational, reputational, technological, and compliance risks. This allows organizations to have a comprehensive view of risks and manage them under a single strategy.
- Risk management process: risk management occurs at all organizational levels and starts with strategy development. This process includes:
- Defining acceptable risk levels
- Identifying and categorizing risks
- Assessing the company’s exposure to risks
- Developing risk management strategies
- Integration into strategic planning: enterprise risk management strategy integrates risk management into strategic planning, enabling more informed decision-making and adaptability to changing conditions.
- Monitoring and adaptation: continuous risk monitoring and adaptation to new threats and opportunities are crucial elements of ERM. This helps organizations remain flexible and prepared for changes.
- Reporting: enterprise risk management system facilitates the creation of consolidated risk reports, providing senior management with timely information for decision-making.
Core components of ERM
- Policies and procedures: documented rules and instructions that describe how an organization manages risks, ensuring a uniform approach to risk identification, assessment, monitoring, and management.
- Risk identification: the process of identifying potential threats that could impact the organization’s goals. This includes analyzing both internal and external environments.
- Risk assessment: determining the likelihood and potential impact of each risk. Prioritizing risks based on their significance and business impact.
- Risk management: developing and implementing strategies to minimize, eliminate, or transfer risks. Identifying responsible individuals for managing specific risks.
- Monitoring and reporting: continuously tracking changes in risk levels and the effectiveness of measures. Regularly providing reports to management to inform them about the current risk status and mitigation measures.
- Technological tools: using specialized software for data collection, risk analysis, process automation, and report creation. Integrating with other corporate systems to ensure a comprehensive approach to risk management.
The Importance of ERM for Business: Benefits, Limitations, and Drawbacks
Enterprise risk management (ERM) is indispensable for businesses as it offers a structured approach to identifying and controlling risks, thereby minimizing their impact. This helps companies avoid financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
What is ERM in business
Here are some key reasons why ERM is crucial:
- Risk identification and control: ERM enables companies to identify potential threats and mitigate their impact, safeguarding against financial losses, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
- Better resilience: systematically managing risks, companies become more resilient to external and internal changes, allowing them to respond quickly to new market conditions, economic crises, legislative changes, and technological shifts.
- Enterprise risk and compliance: ERM plays a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Companies with effective risk management mechanisms are better equipped to pass audits, reduce the likelihood of fines, and avoid legal disputes.
- Improved strategic planning: integrating ERM into decision-making processes helps identify not only threats but also new opportunities. This enables management to allocate resources more effectively, choose the most efficient strategies, and achieve long-term goals.
- Increased investor and customer trust: transparent risk management strengthens trust in a company. Investors, customers, and partners see that the business carefully controls its processes, boosting their confidence in the organization’s reliability.
Limitations and drawbacks of ERM
While ERM offers numerous benefits, it also comes with some challenges:
- High initial costs: implementing ERM requires significant investments in resources, staff training, and technology. This can be a barrier for smaller organizations or those with limited budgets. Demonstrating the value of ERM through cost-benefit analyses can help justify these expenses.
- Complexity of implementation: creating an effective risk management system can be time-consuming and demands considerable effort from the team. It involves developing comprehensive policies, procedures, and frameworks that align with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Potential employee resistance: some team members may resist changes or fail to understand the importance of the new system. This resistance can arise from past experiences or concerns about job security due to automation. Effective communication and involving employees in the implementation process can mitigate this challenge.
- Risk of over-control: an excessive focus on risks can sometimes lead to slowed processes and reduced business flexibility. Balancing enterprise management risk with operational efficiency is crucial to avoid stifling innovation or responsiveness to market changes
- Lack of management support: without strong support from top management, ERM initiatives may struggle to gain traction. Communicating the strategic benefits of the enterprise risk management model and aligning it with organizational goals can help secure necessary resources and buy-in.
- Defining and quantifying risks: establishing a consistent risk definition and framework can be challenging. This involves identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks effectively, which is essential for a successful enterprise risk management plan.
Despite these challenges, the advantages of enterprise risk management framework often outweigh the drawbacks, making it a valuable tool for businesses seeking to heighten their resilience and competitiveness.
How Enterprise Risk Management Works
Enterprise risk management (ERM) provides organizations with a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and managing risks across all business functions. Unlike traditional risk management, which often focuses on isolated risks, ERM takes a holistic view, ensuring that risks are aligned with strategic objectives and business goals. By integrating risk management into decision-making processes, organizations can proactively address uncertainties, minimize potential threats, and capitalize on opportunities.
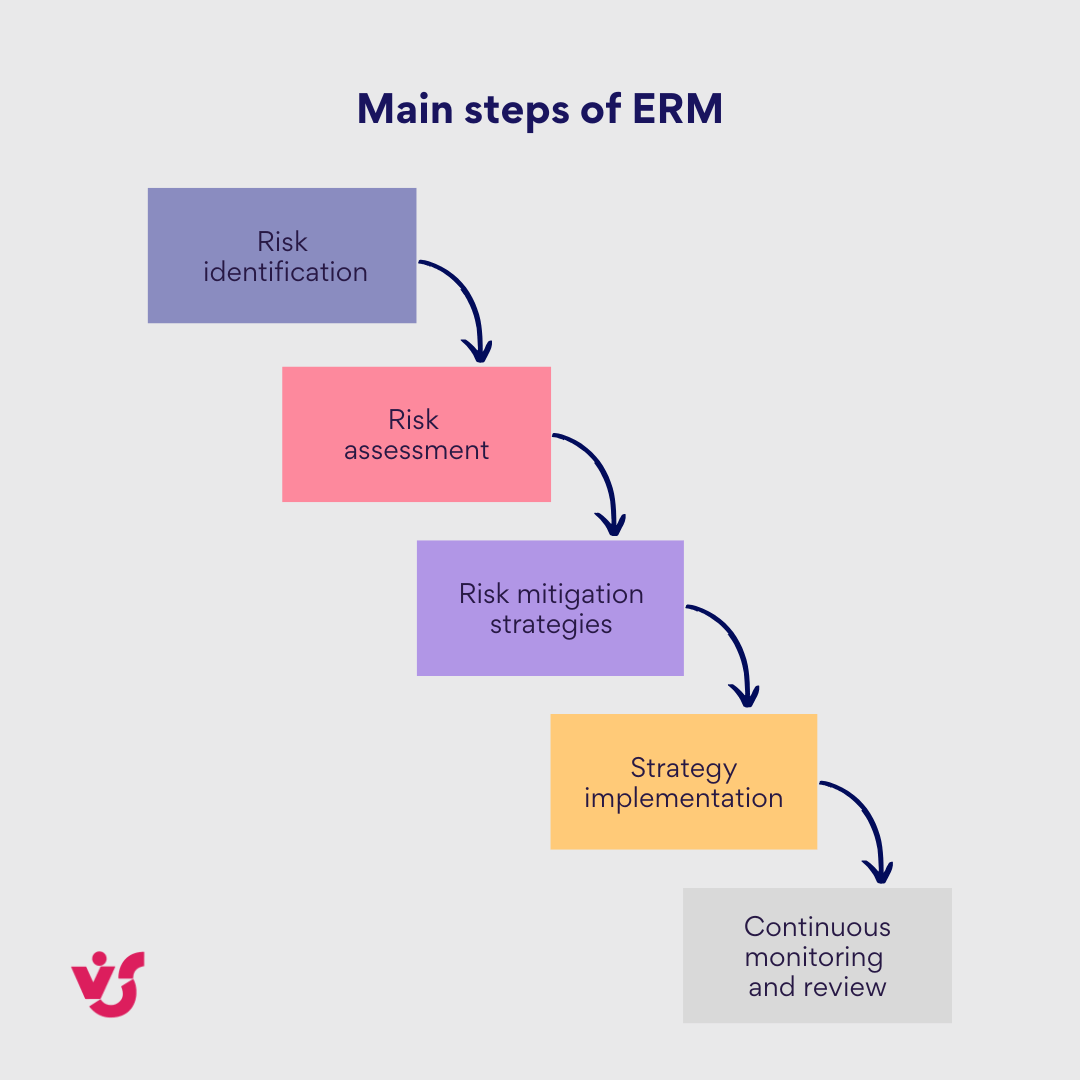
Main steps of ERM
The enterprise risk management process involves several critical steps designed to systematically manage risks across an organization. Here are the primary stages:
- Risk identification
Internal and external analysis: this step involves recognizing potential threats that could impact the organization’s objectives. It includes analyzing both internal and external environments to pinpoint risks. Internal risks might include operational inefficiencies or talent shortages, while external risks could be market fluctuations or regulatory changes.
Risk categories: risks are typically categorized into types such as financial, operational, reputational, strategic, and technological risks. This categorization helps in understanding the nature of risks and their potential impact.
- Risk assessment
Impact and likelihood evaluation: evaluating the potential impact and likelihood of each identified risk. This step helps prioritize risks based on their significance and potential business impact. Tools like risk matrices are often used to visualize and prioritize risks.
Quantitative and qualitative analysis: both quantitative (e.g., financial impact) and qualitative (e.g., reputational damage) analyses are conducted to ensure a comprehensive understanding of each risk.
- Risk mitigation strategies
Risk management options: determining ways to reduce or manage risks. This might involve strategies to minimize, eliminate, or transfer risks. For example, risks can be minimized through process improvements, eliminated by avoiding certain activities, or transferred through insurance or outsourcing.
Cost-benefit analysis: conducting a cost-benefit analysis to ensure that the cost of implementing risk mitigation strategies does not outweigh the potential benefits.
- Strategy implementation
Action plan development: putting the chosen risk management strategies into action. This includes developing detailed action plans that outline specific steps to be taken.
Resource allocation and responsibility assignment: assigning responsibilities and allocating necessary resources to ensure effective execution. This might involve training personnel or investing in technology to support risk management efforts.
- Continuous monitoring and review
Risk monitoring: regularly tracking changes in risk levels and the effectiveness of implemented strategies. This involves setting up monitoring systems to detect early signs of risk escalation or changes in risk profiles.
Review and adjustment: conducting regular reviews to assess the effectiveness of risk management strategies and making timely adjustments and improvements as needed. This ensures that the risk management approach remains relevant and effective over time.
Tools and methodologies used in ERM
Several tools and methodologies can accelerate the ERM process, ensuring that organizations are well-equipped to manage risks effectively. Here are some of the key tools and methodologies used in ERM:
- Scenario analysis
- Hypothetical scenario development: this involves creating hypothetical scenarios to predict how different risks might play out. It helps organizations prepare for potential future events, such as economic downturns, natural disasters, or technological disruptions.
- Strategic planning: Having analyzed these scenarios, organizations can develop strategic plans to mitigate potential risks and capitalize on opportunities. This proactive approach ensures that companies are prepared for a wide range of possible outcomes.
- Stakeholder engagement: scenario analysis often involves engaging with various stakeholders, including employees, customers, and suppliers, to gather insights and validate assumptions about potential future scenarios.
- Risk matrix development
- Visual risk categorization: creating a matrix to visually categorize risks based on their likelihood and potential impact. This tool aids in prioritizing risks and allocating resources effectively.
- Prioritization: the risk matrix helps prioritize risks by plotting them against their likelihood and potential impact, allowing organizations to focus on the most critical risks first.
- Resource allocation: after categorizing risks, organizations can allocate resources more efficiently, ensuring that high-priority risks receive adequate attention and mitigation efforts.
- Regular audits and testing
- Compliance and effectiveness: conducting periodic audits and tests to ensure that risk management strategies are working as intended. This helps identify gaps and areas for improvement in the risk management framework.
- Gap analysis: audits and tests provide insights into whether current risk management practices align with organizational objectives and regulatory requirements. This helps in identifying any gaps between current practices and desired outcomes.
- Continuous improvement: regular audits facilitate continuous improvement by providing feedback on the effectiveness of risk management strategies. This feedback loop ensures that risk management processes remain relevant and effective over time.
- Risk assessment templates and checklists
- Structured risk identification: these tools provide a structured format for identifying and recording potential risks. They help ensure that all relevant risks are considered and documented systematically.
- Consistency: using templates and checklists ensures consistency in risk assessment across different departments and projects, reducing the likelihood of overlooking critical risks.
- Risk analysis software
- Advanced risk analysis: utilizing software applications that employ statistical models and simulations, such as Monte Carlo simulations, to analyze risk scenarios and their potential impacts. This provides a more objective and detailed understanding of risks.
- Data-driven decision making: These tools enable organizations to make data-driven decisions by quantifying risks and predicting outcomes, which is essential for strategic planning and resource allocation.
- Project management software
- Integrated risk management: many project management tools offer integrated risk management features, allowing organizations to track risks alongside project milestones. This ensures that risk management is aligned with operational objectives.
- Real-time monitoring: these tools facilitate real-time monitoring of risks, enabling prompt responses to changes in risk levels or new risk emergence.
- Financial risk management tools
- Financial risk focus: these tools are specifically designed to identify and mitigate risks related to financial operations, such as market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk. They help organizations manage financial exposures effectively.
- Regulatory compliance: financial risk management tools also ensure compliance with financial regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Enterprise risk management (ERM) software
- Comprehensive risk management: ERM software provides a comprehensive platform for identifying, assessing, and managing risks across the organization. It integrates risk management into corporate strategy, ensuring that risk considerations are embedded in decision-making processes.
- Centralized risk management: these platforms offer centralized risk management, allowing organizations to monitor and manage risks across different departments and business units from a single interface.
Enterprise Risk Management Programs in Organizations
Enterprise risk management (ERM) programs are essential for organizations to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate risks that could impact their objectives. These programs provide a structured approach to managing uncertainties while aligning risk management with business strategy and decision-making.
What is an ERM program and its benefits
An enterprise risk management program is a structured plan designed to implement risk management practices across all levels of an organization. It involves developing policies, training staff, setting up monitoring systems, and providing regular reports to management. An effective ERM program not only helps companies reduce existing risks but also enables them to adapt more quickly to new challenges.
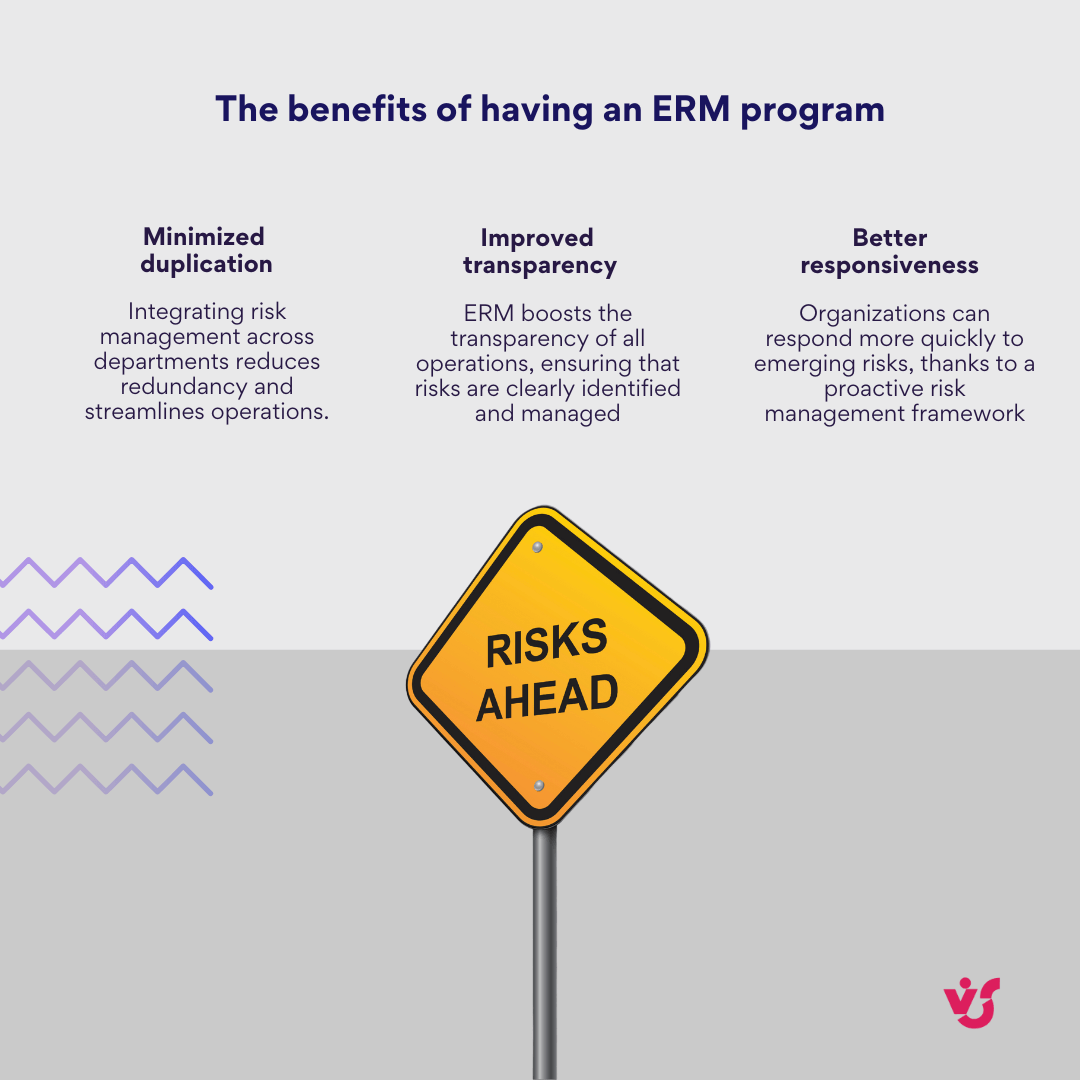
The benefits of having an ERM program include:
- Reduced duplication of efforts: through integrating risk management across departments companies can avoid redundant efforts and streamline their operations.
- Improved transparency: ERM boosts the transparency of all operations, ensuring that risks are clearly identified and managed.
- Better responsiveness: organizations can respond more quickly to emerging risks, thanks to a proactive risk management framework.
👉What is an enterprise risk management program? An enterprise risk management (ERM) program is a structured framework that organizations use to identify, assess, manage, and monitor risks across all business areas, ensuring alignment with strategic objectives and risk appetite. It involves recognizing internal and external risks, evaluating their likelihood and impact, developing mitigation strategies, and continuously tracking and reporting risks to support informed decision-making. By integrating risk management into corporate strategy and daily operations, an ERM program encourages resilience and helps organizations proactively address uncertainties.
Examples of ERM application across different industries
ERM is applied in various sectors to manage industry-specific risks and challenges. Here are some examples:
- Financial sector: a bank implements ERM to track credit and market risks. Analyzing potential defaults and currency fluctuations, it minimizes financial losses and ensures regulatory compliance.
- Healthcare: a medical organization uses ERM to manage patient safety risks. This includes analyzing cases of non-compliance with care standards, managing medical waste, and ensuring patient data confidentiality.
- Manufacturing: a factory implements ERM to monitor production risks. Regular assessments of equipment conditions and workplace safety reduce the likelihood of accidents, minimize downtime, and ensure compliance with labor safety norms.
- Information Technology: an IT company applies ERM to manage cyber risks. It assesses cyberattack threats, develops incident response plans, and conducts regular security audits of its systems.
- Energy and oil/gas: an energy company uses ERM to analyze risks associated with oil extraction and transportation. This helps prevent environmental disasters, comply with environmental regulations, and minimize costs related to accident mitigation.
- Retail: a large retail chain uses ERM to manage logistical and operational risks. Analyzing potential supply chain disruptions and seasonal demand fluctuations allows for timely adjustments in procurement and delivery strategies.
These examples illustrate how ERM can be tailored to meet the unique challenges of different industries, strengthening adaptability and strategic decision-making across diverse sectors.
The Role of Virtosoftware Products in Risk Management
Virtosoftware offers a range of products that help enterprises manage risks more effectively. These tools hone the risk management process by streamlining critical tasks and ensuring timely action.
How Virtosoftware products support risk management
This tool allows organizations to coordinate audit schedules and compliance checks, minimizing the likelihood of missing important events. By keeping track of all upcoming audits and regulatory deadlines, companies can ensure they are always prepared. Compatible with SharePoint Online & Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Teams.
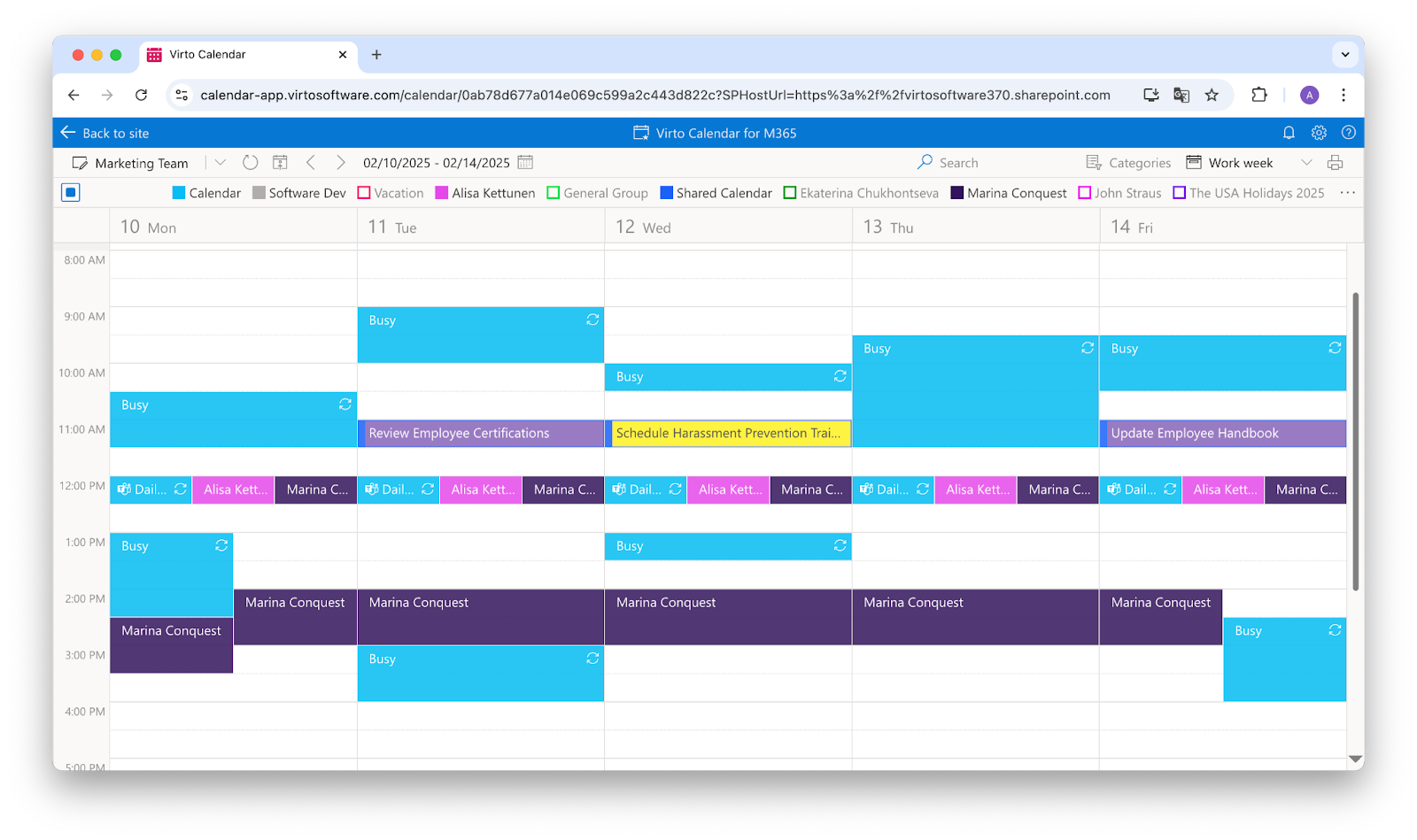
This product provides timely notifications about potential risks and deadlines, helping prevent problems before they arise. By staying informed about critical dates and potential threats, organizations can take proactive measures to mitigate risks.
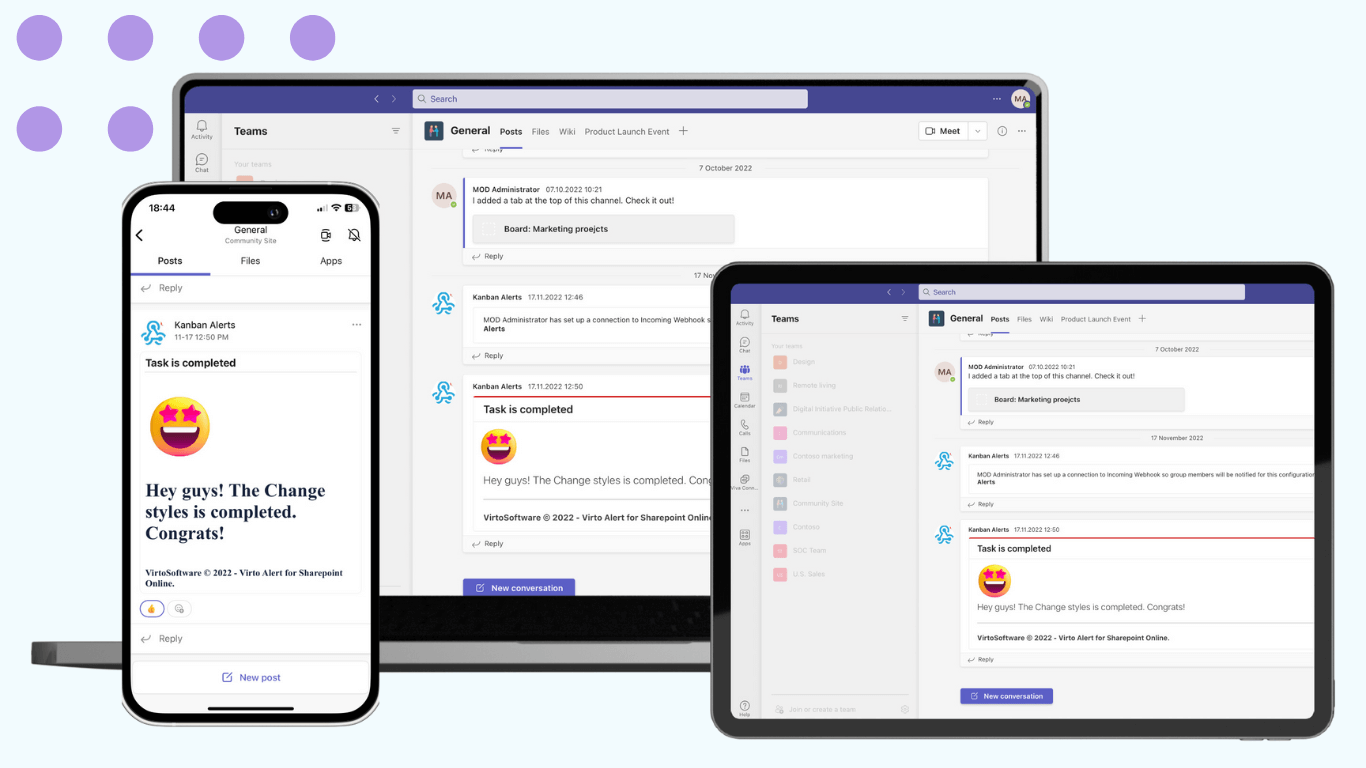
This solution simplifies document management by providing secure storage and access to files necessary for audits. Centralizing documentation ensures that all relevant information is readily available when needed, reducing the risk of non-compliance or data loss. Available for SharePoint Online & Microsoft 365 and SharePoint On-Premises.
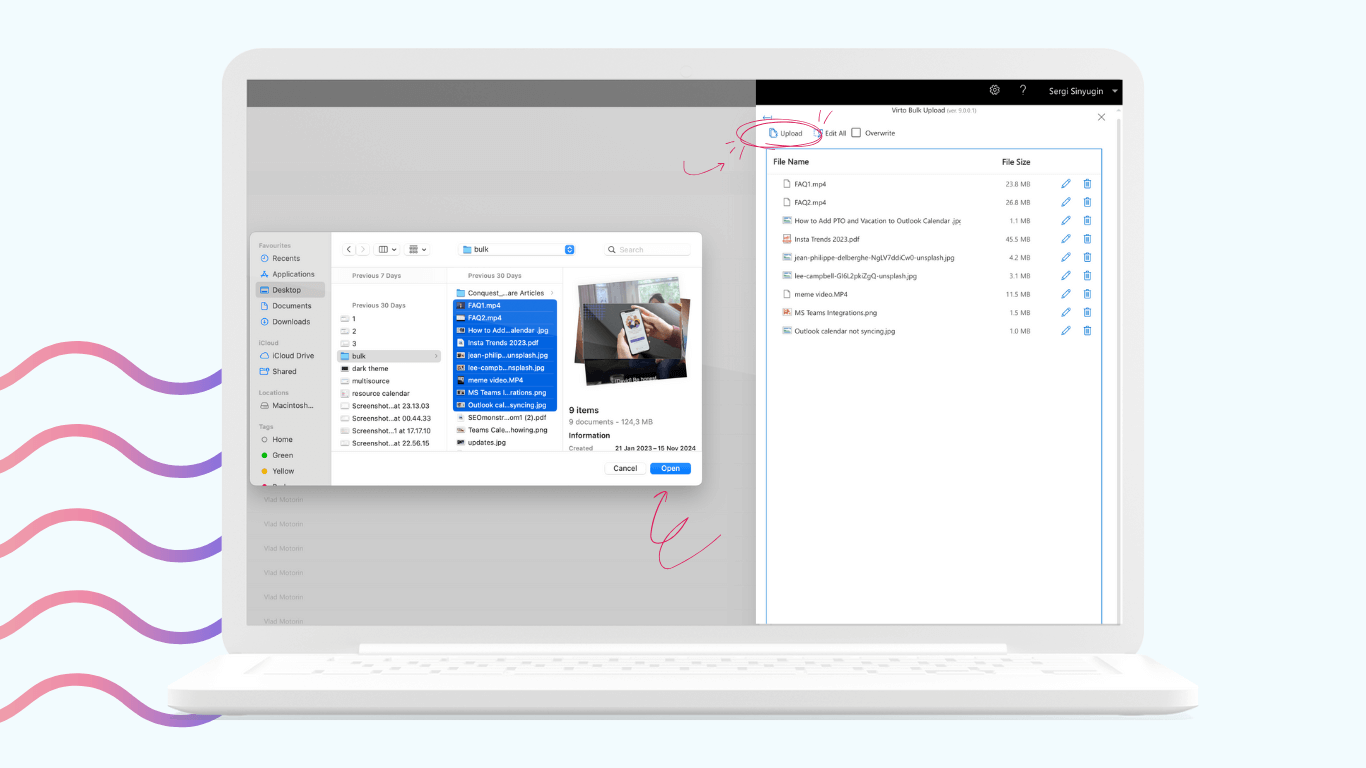
Examples of using Virtosoftware products
VirtoSoftware offers a range of productivity and collaboration tools designed to streamline business processes within Microsoft 365 and SharePoint environments. Below are the examples of how VirtoSoftware products can be applied in real-world scenarios.
Coordinating regular compliance checks with Virto calendar app
Scheduling audits and compliance checks: through scheduling audits and compliance checks in advance using Virto Calendar App, companies can ensure they meet all regulatory requirements on time. This helps maintain a smooth operation and avoids potential fines or reputational damage. With iCalendar support, organizations can even track compliance deadlines beyond the M365 environment.
Centralized management: the app allows organizations to centralize all compliance-related tasks in one platform, eliminating the need to manage multiple calendars. This ensures that all stakeholders are informed and aligned with upcoming audits and checks.
Automated reminders: Virto Calendar App can be integrated with Virto Alerts & Reminders to send automated notifications about upcoming deadlines, ensuring that teams are prepared well in advance. Microsoft Outlook integration allows users to schedule customized email alerts, from immediate notifications to weekly summaries.
Deadline notifications with Virto Alerts & Reminders
Timely reminders: timely reminders about upcoming deadlines help organizations stay on track and avoid missed opportunities or penalties. This proactive approach ensures that all critical tasks are completed before they become urgent. Teams can receive real-time notifications directly in Microsoft Teams channels, keeping everyone informed within their collaborative workspace.
Customizable notifications: the app allows for customizable notifications, enabling organizations to tailor alerts based on specific risk management needs. For example, reminders can be set for risk assessment reviews, compliance filings, or audit preparations. Microsoft SharePoint integration ensures users stay updated on changes in SharePoint lists, so no critical update goes unnoticed.
Integration with other tools: Virto Alerts & Reminders can be integrated with other Virtosoftware tools, such as Virto Calendar App, to create a seamless risk management workflow. Alerts can also be scheduled to sync with iCalendar, ensuring visibility across different calendar systems.
Centralized document storage with Virto Multiple File Upload App
Efficient audit preparation: during audits, having all necessary documents easily accessible can significantly reduce stress and improve efficiency. Virto Multiple File Upload App provides a centralized document storage solution, ensuring that all relevant files are secure, organized, and readily available.
Secure access: the app offers secure access controls, allowing organizations to manage who can view or edit documents. This is particularly important for sensitive compliance documents that require restricted access. Integration with Microsoft SharePoint allows organizations to automatically set alerts for changes in SharePoint lists, ensuring compliance teams are always informed of updates.
Streamlined audit process: having all necessary documents in one place, organizations can streamline the audit process, making it smoother and less prone to errors. This reduces the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties. Notifications can also be sent via Microsoft Outlook or Microsoft Teams, ensuring key stakeholders remain informed and responsive.
By integrating these Virtosoftware products into their risk management strategies, businesses can enhance their ability to identify, assess, and mitigate risks effectively. These tools help ensure compliance, improve operational efficiency, and reduce the likelihood of missed deadlines or regulatory breaches.
Wrapping Up
Enterprise risk management (ERM) is the secret sauce that helps businesses stay on top of their game. Implementing a solid ERM program companies can dodge potential pitfalls and supercharge their operations. It’s not just about avoiding risks; it’s about setting yourself up for long-term success.
As we’ve explored in this article, the definition of enterprise risk management is all about being proactive and managing risks across every aspect of your business. It’s like having a crystal ball that helps you anticipate challenges and make informed decisions.
To take your risk management to the next level, we recommend checking out Virtosoftware’s tools. They can help streamline your processes, keep you on top of compliance, and ensure you’re ready for whatever comes next.
👉For a closer look at how Virtosoftware can support your ERM efforts, be sure to check out our use case.
👉For more insights and practical tips, be sure to check out additional guides on our blog: