Effective cross-departmental collaboration, fueled by clear communication and shared goals, is the bedrock of a successful organization. When departments operate in silos, crucial information gets lost, projects stall, and opportunities are missed.
This article explores the vital role of cross-departmental collaboration in driving organizational success.
We’ll delve into real-world examples of successful collaboration, highlighting the tangible benefits it brings, from increased innovation and efficiency to improved employee morale and customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, we’ll provide practical recommendations for breaking down departmental barriers and fostering a collaborative culture.
Finally, we’ll examine specific tools designed to enhance collaboration within and across departments, including the Virto Calendar App for SharePoint Online & Microsoft 365 and the Virto Calendar App for Microsoft Teams, showcasing how technology can facilitate communication and streamline workflows for optimal results.
What Is Cross-Departmental Collaboration?
In this section, we’ll explore the fundamental concepts of cross-departmental collaboration, its significance in modern organizations, and how it differs from other forms of organizational cooperation. Understanding these concepts is essential for building effective collaborative frameworks that drive business success.
Definition, goals, and objectives of cross-departmental collaboration
Cross-departmental collaboration refers to the structured cooperation between different departments or business units within an organization to achieve common goals and objectives. This collaborative approach involves teams from various departments working together, sharing resources, knowledge, and expertise to solve complex business challenges and deliver value to stakeholders.
The primary goals of cross-departmental collaboration include:
- Breaking down organizational silos to foster innovation and creativity
- Leveraging diverse expertise and perspectives to solve complex problems
- Streamlining processes and reducing redundancies across departments
- Creating unified approaches to achieve organizational objectives
- Enhancing knowledge sharing and organizational learning
👉 What is cross departmental meaning? Cross-departmental refers to activities, communication, or collaboration that involves multiple departments within an organization. It breaks down silos between different teams, fostering a more integrated and collaborative work environment. This approach facilitates the sharing of knowledge, resources, and perspectives across different functional areas. Ultimately, cross-departmental efforts contribute to improved efficiency, innovation, and overall organizational success. It contrasts with working in isolation within individual departments.
Why is cross-departmental collaboration important?
Cross-departmental collaboration serves as a catalyst for organizational success in several crucial ways. First, it enables organizations to respond more effectively to complex business challenges that require diverse expertise and perspectives. When departments work together seamlessly, they can tackle multifaceted projects more efficiently and deliver better results.
The importance of cross-departmental collaboration is evident in its impact on resource utilization and productivity. When departments collaborate effectively, they can:
- Share resources more efficiently, reducing waste and redundancy
- Accelerate decision-making processes through improved communication channels
- Identify and implement best practices across the organization
- Foster innovation through the cross-pollination of ideas and approaches
Perhaps most importantly, cross-departmental collaboration directly affects customer service quality. When departments communicate and work together effectively, they can:
- Provide more comprehensive solutions to customer needs
- Reduce response times to customer inquiries and issues
- Ensure consistent messaging and service delivery across all customer touchpoints
- Anticipate and address potential problems before they impact customers
👉 What is cross-departmental coordination? Cross-departmental coordination is the organized alignment of activities and resources between different departments to achieve a shared outcome. It involves streamlining processes, establishing clear communication channels, and ensuring that all teams are working in sync. Effective coordination minimizes conflicts, reduces redundancies, and maximizes efficiency across departments. This structured approach ensures that all departments contribute effectively to the overall organizational goals.
Difference between cross-departmental collaboration and interdepartmental collaboration
While often used interchangeably, cross-departmental and interdepartmental collaboration have distinct characteristics and applications. Cross-departmental collaboration typically involves multiple departments working together on shared projects or initiatives, with team members from different departments forming temporary or permanent cross-functional teams.
In contrast, interdepartmental collaboration often refers to more routine interactions and information sharing between departments that maintain their separate structures and primary responsibilities. For example:
Cross-departmental collaboration:
- A product development team comprising members from R&D, Marketing, Sales, and Customer Service working together to launch a new product
- A cross-functional task force formed to implement a new enterprise-wide software system
Interdepartmental collaboration:
- Marketing department sharing customer feedback with the Product Development team
- Finance department providing budget updates to various department heads
The key distinction lies in the level of integration and shared responsibility. Cross-departmental collaboration involves deeper integration and shared accountability for outcomes, while interdepartmental collaboration typically maintains clearer departmental boundaries while facilitating necessary information exchange and coordination.
Here’s a comprehensive comparison of interdepartmental vs. cross-departmental collaboration for your easy reference:
| Aspect | Interdepartmental Collaboration | Cross-Departmental Collaboration |
| Structure | Maintains clear departmental boundaries and hierarchies | Forms fluid, cross-functional teams that transcend traditional department boundaries |
| Integration level | Lower—departments remain distinct entities working together | Higher—teams are integrated into cohesive units regardless of department origin |
| Duration | Often ongoing but intermittent, based on routine needs | Can be temporary (project-based) or permanent (strategic initiatives) |
| Decision making | Typically follows traditional hierarchical channels | More collaborative and consensus-based across department lines |
| Resource allocation | Resources remain within departmental control | Resources are pooled and shared across departmental boundaries |
| Communication flow | Formal channels between department heads or designated liaisons | Direct communication between team members regardless of department |
| Project ownership | Clear departmental ownership with supporting roles from other departments | Shared ownership and responsibility across departments |
| Goals | Department-specific goals with consideration for other departments’ needs | Shared objectives that benefit the entire organization |
| Team structure | Team members report to their respective department heads | Team members may report to project leaders outside their department |
| Knowledge sharing | Structured sharing of information between departments | Organic knowledge exchange through daily collaboration |
| Culture impact | Maintains traditional departmental cultures | Creates a unified collaborative culture across departments |
| Examples | • Monthly reports from Finance to other departments • HR sharing policy updates with all departments • IT providing technical support to various departments | • Cross-functional product development teams • Organization-wide digital transformation initiatives • Customer experience improvement taskforce |
| Primary focus | Coordination and information exchange | Integration and joint problem-solving |
| Performance metrics | Department-specific KPIs with some shared metrics | Shared KPIs focused on collective outcomes |
| Challenge level | Lower—follows established protocols | Higher—requires more coordination and change management |
👉 How do you collaborate across departments? Collaboration across departments starts with establishing clear communication channels and shared goals. Regular meetings, shared platforms, and collaborative tools facilitate information sharing and joint problem-solving. Assigning clear roles and responsibilities ensures accountability and avoids duplication of effort. Building relationships and fostering a culture of mutual respect encourages open communication and trust between teams.
Benefits of Cross-Departmental Collaboration
Cross-departmental collaboration offers numerous advantages that extend far beyond basic operational efficiency. In this section, we’ll explore the key benefits that organizations can realize when they successfully implement cross departmental collaboration, from enhanced communication and innovation to improved employee satisfaction and customer service outcomes.
Improved cross department communication
When departments work together effectively, communication barriers naturally dissolve. Instead of information getting stuck in departmental silos or lost in lengthy email chains, cross-departmental collaboration creates direct channels for information sharing. For example, when Marketing and Product Development teams collaborate closely, product updates reach the market faster, and customer feedback flows more quickly back to the development team. This improved communication flow not only speeds up processes but also reduces misunderstandings and ensures all stakeholders remain aligned with project goals.
Teamwork
Cross-departmental collaboration democratizes the idea-generation process, creating an environment where insights are valued regardless of their source. A junior customer service representative might provide crucial insights that help the product development team solve a persistent issue, while a marketing analyst might offer valuable perspective on technical features. This inclusive approach to teamwork strengthens organizational cohesion and creates a more unified company culture where every voice matters.
Increased employee engagement
When employees collaborate across departmental lines, they gain a broader perspective of how their work contributes to the organization’s overall mission. For instance, when finance team members work directly with operations on process improvement initiatives, they better understand how their financial analyses impact day-to-day operations. This enhanced understanding creates a stronger connection to the company’s mission and increases overall engagement.
Increased productivity
Cross departmental collaboration significantly reduces redundant efforts and streamlines workflows. When departments work in isolation, they often duplicate tasks or create processes that conflict with other departments’ workflows. Through collaboration, teams can identify these inefficiencies and develop streamlined approaches. For example, when Sales and Marketing teams collaborate closely, they can create unified customer outreach strategies instead of running parallel, potentially contradictory campaigns.
Fostering innovation
The intersection of different departmental perspectives often sparks innovation. When diverse teams with varying expertise come together, they bring different approaches to problem-solving and creativity. A collaboration between IT and HR might lead to innovative solutions for employee onboarding, while partnerships between Operations and Customer Service could generate new ways to improve service delivery.
Solving complex problems
Cross-departmental collaboration is particularly effective at addressing multifaceted challenges that no single department could solve alone. For instance, addressing supply chain disruptions might require input from Procurement, Logistics, Finance, and Customer Service departments. Each team brings unique insights and capabilities to the table, leading to more comprehensive and effective solutions.
Employee satisfaction
When employees participate in cross-departmental initiatives, they often experience increased job satisfaction through broader exposure to different aspects of the business and recognition of their contributions. This collaborative environment shows employees that their ideas and efforts are valued beyond their immediate department, leading to higher morale and improved retention rates. For example, when a customer service representative’s suggestion leads to a product improvement, their sense of value and contribution to the company increases significantly.
Improved customer service
Perhaps one of the most significant benefits is the impact on customer service quality. When departments collaborate effectively, customers experience seamless service across all touchpoints. For instance, when Sales, Support, and Product teams work together closely, customers receive consistent information and faster resolution to their issues. This coordinated approach leads to higher customer satisfaction, increased loyalty, and more positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Through these various benefits, cross departmental collaboration creates a positive cycle of improvement: better communication leads to increased innovation, which results in improved customer satisfaction, leading to higher employee morale, and so on. Organizations that successfully implement cross-departmental collaboration often find these benefits compound over time, creating sustainable competitive advantages in their markets.
How to Improve Cross-Departmental Collaboration
This section will delve into the common challenges that organizations face when implementing cross-departmental collaboration and outline effective strategies for overcoming these obstacles and fostering a truly collaborative environment.
What are the cross-departmental issues?: Challenges of cross-departmental collaboration
While the benefits are numerous, cross-departmental collaboration can present certain challenges:
- Lack of trust between departments: This can be a significant barrier. It often stems from a lack of transparency in communication, competition for resources or recognition, or simply a lack of experience working with other departments. Pre-existing departmental rivalries can further exacerbate this issue.
- Differences in priorities and goals: Each department has its own objectives, which may not always align with those of other departments. For instance, the sales team might prioritize short-term sales targets, while the marketing team focuses on long-term brand building. Differences in project management approaches and preferred communication styles can also lead to misunderstandings and friction.
- Limited resources and time: Departments often operate under tight deadlines and with limited budgets and staff. Engaging in cross-departmental projects can strain these resources further, leading to overworked employees, compromised work quality due to insufficient time for thorough completion of tasks, and delays in project delivery.
- Communication issues: Poor communication can derail even the best-laid plans. Insufficient or unclear communication can lead to misunderstandings about goals and objectives, duplication of work, omission of crucial details, and increased conflict due to the lack of a shared platform for discussions and decision-making.
By acknowledging and actively addressing these challenges, organizations can better prepare for successful cross departmental collaboration and create more effective strategies for overcoming potential obstacles.
Strategies for solving problems in cross department collaboration
Successfully addressing collaboration challenges requires a systematic approach and well-defined strategies. This section explores ten key strategies that organizations can implement to enhance cross departmental communication and overcome common obstacles.
Clear definition of goals, roles, and KPIs
Establishing clear objectives and responsibilities is fundamental to successful cross-departmental collaboration. Organizations should create SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals that align different departments’ efforts. For each collaborative initiative, clearly define:
- Specific project objectives and expected outcomes
Organizations must define concrete, unambiguous goals that all departments can understand and align with, ensuring everyone is working toward the same vision. Each phase of the project should have clearly outlined deliverables and success criteria, providing tangible targets for teams to work toward. A comprehensive project scope statement must identify both what is included and excluded from the initiative, preventing scope creep and misalignment. Every department’s contribution should be explicitly tied to the overall objective, helping team members understand how their work fits into the broader picture. Finally, clear end-state descriptions should define what success looks like from all departmental perspectives, ensuring alignment on the desired outcome.
- Individual and departmental responsibilities
Implementing detailed RACI matrices (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) for all team members creates clarity around roles and decision-making authority in cross-departmental projects. Clear reporting structures and decision-making authorities need to be established to prevent confusion and delays in project execution. Organizations should establish well-defined escalation paths for issue resolution, ensuring problems are addressed efficiently at the appropriate level. Specific task ownership and handoff procedures between departments must be documented to ensure smooth transitions and prevent work from falling through the cracks. To ensure project continuity, backup responsibilities for critical roles should be outlined, allowing work to continue seamlessly even when key team members are unavailable.
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) that measure collaborative success
Organizations must develop specific metrics that directly measure the effectiveness of cross department collaboration, going beyond traditional departmental performance measures. Balanced scorecards should be created to consider and weigh the contributions of all departments, ensuring fair and comprehensive performance assessment. Both leading and lagging indicators need to be established to track progress, with leading indicators helping predict future success and lagging indicators measuring actual achievements. Regular KPI review sessions should be conducted with all involved departments to maintain alignment and address any performance gaps. Clear threshold levels must be defined that automatically trigger corrective actions when metrics fall below acceptable levels, ensuring proactive problem-solving.
- Timeline and milestones for project completion
Detailed project schedules must be created with clear identification of dependencies between departments, helping teams understand how their timelines impact other groups. Checkpoint milestones requiring multi-department sign-off should be established at critical project stages, ensuring all departments agree on progress and readiness to proceed. Adequate buffer time needs to be incorporated into schedules for cross-departmental reviews and approvals, preventing rushed decisions and allowing for thorough collaboration. Critical path activities that impact multiple departments should be clearly defined and closely monitored, as delays in these areas can affect the entire project timeline. Regular schedule review and adjustment procedures need to be established to keep the project on track and address any timeline challenges proactively.
- Resource allocation and budget responsibilities
Detailed resource plans showing shared resource commitments across departments must be created to prevent overallocation and ensure efficient use of company assets. Clear cost-sharing agreements between departments need to be established upfront to prevent budget disputes and ensure fair distribution of expenses. Well-defined procedures for requesting additional resources or budget should be implemented, allowing departments to obtain needed support without unnecessary delays. Approval processes for shared expenses must be documented clearly to streamline decision-making and maintain accountability. Robust tracking mechanisms for resource utilization across departments should be implemented to monitor efficiency and identify areas for optimization.
Organizing regular meetings, conferences, and workshops
Structured communication opportunities are essential for maintaining alignment and momentum in cross-departmental initiatives. However, these meetings must be purposeful and well-organized to be effective:
- Schedule regular status updates with clear agendas
Regular status updates should be scheduled with clear, well-distributed agendas that outline specific discussion points and expected outcomes. These agendas should be shared in advance to allow participants to prepare effectively and contribute meaningfully to the discussion. The practice of distributing agendas also helps team members determine whether their presence is truly necessary, respecting everyone’s time.
- Implement standing meetings at consistent times to ensure availability
Standing meetings should be implemented at consistent times, allowing team members to block these times in advance and ensuring maximum availability across departments. When meetings occur at predictable intervals, departments can better plan their work around these collaborative touchpoints and maintain consistent participation. This regularity also helps establish collaboration as a core part of the organizational routine rather than an afterthought.
- Use different meeting formats (brief daily stand-ups, weekly progress reviews, monthly strategic discussions)
Organizations should utilize different meeting formats to address varying collaborative needs effectively. Brief daily stand-ups can keep teams aligned on immediate priorities and challenges, while weekly progress reviews provide opportunities for more detailed discussion of ongoing initiatives. Monthly strategic discussions allow departments to step back from day-to-day operations and focus on longer-term goals and strategic alignment. Each format serves a distinct purpose in maintaining effective cross departmental communication.
- Document and distribute meeting outcomes and action items
Meeting outcomes and action items must be thoroughly documented and distributed promptly to all relevant stakeholders. This documentation should include key decisions made, responsibilities assigned, deadlines established, and any important discussion points that impact multiple departments. Clear documentation ensures that all participants have the same understanding of what was decided and what needs to be done, preventing misunderstandings and keeping projects on track.
- Ensure meetings have clear objectives and stay focused on relevant topics
Every meeting should have clear objectives and maintain focus on relevant topics throughout the discussion. Meeting facilitators need to be skilled at managing conversations to prevent drift into unrelated areas while ensuring all necessary topics receive adequate attention. When meetings stay focused on their intended purpose, they become more valuable and respected as essential tools for cross departmental collaboration rather than time-consuming obligations.
Improve communication between departments
Creating dedicated spaces for collaboration, both physical and digital, is crucial for fostering effective communication:
- Establish collaboration zones where teams can work together informally
Establishing collaboration zones where teams can work together informally creates opportunities for spontaneous interaction and idea sharing between departments. These spaces should be designed to accommodate both planned and impromptu meetings, featuring flexible furniture arrangements, whiteboards or digital displays for visual collaboration, and adequate space for group discussions. These physical spaces serve as neutral territory where departments can come together outside their usual work areas, breaking down territorial barriers and encouraging natural collaboration.
- Implement project management tools that facilitate cross-departmental workflow
Project management tools that facilitate cross-departmental workflow need to be implemented thoughtfully to ensure smooth coordination between teams. These tools should provide clear visibility into project progress, dependencies, and responsibilities across departments. They should also enable easy task assignment, progress tracking, and resource management while integrating with existing departmental systems to prevent duplicate data entry and maintain consistency across the organization.
- Use shared digital workspaces for real-time collaboration
Shared digital workspaces for real-time collaboration enable teams to work together effectively regardless of their physical location. These platforms should support document sharing, simultaneous editing, and instant communication capabilities. They should also include features for version control, change tracking, and commenting, ensuring that all departments can contribute to and stay updated on shared work products while maintaining accountability and transparency.
- Create standardized communication protocols
Standardized communication protocols must be established to ensure consistent and effective information sharing across departments. These protocols should clearly define appropriate communication channels for different types of information, expected response times, escalation procedures, and documentation requirements. They should also account for different communication needs across departments while maintaining enough standardization to prevent confusion and ensure important information reaches its intended recipients.
- Ensure all team members have access to necessary collaboration tools
Access to necessary collaboration tools must be ensured for all team members across departments. This includes not only providing the right software licenses and hardware but also ensuring adequate training and support for all users. Organizations should regularly assess tool usage and effectiveness, gathering feedback from different departments to identify and address any access or usability issues that might hinder cross-departmental collaboration.
Encourage open communication
Developing channels for open dialogue helps break down barriers and promotes innovation:
- Create digital forums for cross-departmental discussions
Digital forums for cross department discussions should be created to provide accessible platforms where employees from different departments can engage in ongoing conversations about shared projects, challenges, and opportunities. These forums should be well-organized with different sections for various topics, allowing team members to easily find relevant discussions and contribute their insights. The platform should support rich media sharing, threaded discussions, and easy search functionality to make information readily accessible and encourage active participation.
- Implement suggestion systems for improvement ideas
Suggestion systems for improvement ideas need to be implemented in a way that makes it easy for employees to share their thoughts and innovations. These systems should go beyond simple suggestion boxes to include features for collaborative refinement of ideas, voting or rating capabilities, and transparent tracking of suggestion status and implementation progress. The system should also provide clear feedback mechanisms so employees understand how their suggestions are being considered and evaluated.
- Establish channels for anonymous feedback
Channels for anonymous feedback must be established to ensure employees feel comfortable sharing honest opinions without fear of repercussion. These channels should be truly anonymous and secure, with clear guidelines on appropriate use. Organizations should establish regular review processes for anonymous feedback to ensure it receives proper attention and consideration, while also maintaining mechanisms to follow up on important issues without compromising anonymity.
- Host regular open forums for project discussions
Regular open forums for project discussions should be hosted to provide structured opportunities for cross-departmental dialogue. These forums should be scheduled at convenient times for all departments and feature rotating topics that address different aspects of ongoing projects and initiatives. The format should encourage active participation from all attendees, with skilled facilitators ensuring balanced discussion and constructive dialogue.
- Ensure leadership actively participates in and encourages open dialogue
Leadership must actively participate in and encourage open dialogue to demonstrate its importance to the organization. This involves not just attending communication events but actively engaging in discussions, responding to employee input, and modeling the kind of open, honest communication expected from all team members. Leaders should regularly share updates about organizational direction and decision-making processes, while also being receptive to questions and feedback from employees at all levels.
Explore Our Use Cases for Effective Collaboration
Single source of information
Maintaining a centralized information repository ensures all team members work from the same data:
- Implement a document management system
A robust document management system must be implemented to serve as the central repository for all project-related information and documentation. This system should feature intuitive organization structures, powerful search capabilities, and clear categorization of different types of documents. It should also integrate with commonly used business applications and support various file formats while maintaining appropriate security controls to protect sensitive information while still enabling necessary access across departments.
- Create standardized templates for project documentation
Standardized templates for project documentation need to be created and consistently used across all departments to ensure uniformity in how information is captured and presented. These templates should be comprehensive yet flexible enough to accommodate different types of projects and departmental needs. They should include clear sections for key information, standardized formatting, and guidance notes to help users complete them correctly. Regular review and updates of these templates ensure they continue to meet evolving organizational needs.
- Establish clear version control protocols
Clear version control protocols must be established to prevent confusion and ensure everyone works with the most current information. These protocols should define naming conventions, document status indicators, and approval processes for new versions. They should also specify how changes are tracked, who has authority to make updates, and how team members are notified of important document changes. The system should maintain an accessible version history while clearly indicating which version is current.
- Maintain up-to-date project dashboards
Up-to-date project dashboards should be maintained to provide real-time visibility into project status, milestones, and key metrics. These dashboards should be designed to present information in a clear, visually appealing format that makes it easy to quickly understand project progress and identify potential issues. They should include automated data updates where possible to ensure accuracy and reduce manual maintenance effort, while also providing drill-down capabilities for detailed information when needed.
- Ensure easy access to relevant information across departments
Easy access to relevant information across departments must be ensured through well-designed permission structures and intuitive navigation systems. This includes implementing single sign-on capabilities where appropriate, creating clear information hierarchies, and providing multiple ways to find information (such as search, tags, and categorical browsing). Regular audits of access permissions and usage patterns help identify and remove any barriers to information access while maintaining necessary security controls.
Training and skills development
Investing in cross-functional training helps team members better understand and work with other departments:
- Develop cross-training programs between departments
Cross-training programs between departments should be developed to help employees gain practical understanding of how other teams operate and contribute to organizational success. These programs should include structured job shadowing opportunities, hands-on experience with different departmental processes, and regular knowledge-sharing sessions. They should be designed to provide meaningful exposure to other departments’ workflows, challenges, and decision-making processes while maintaining productivity. This deeper understanding helps employees better appreciate how their work impacts other departments and identifies opportunities for improved collaboration.
- Provide training in collaboration tools and techniques
Training in collaboration tools and techniques must be provided to ensure all employees can effectively use the organization’s chosen platforms and systems. This training should go beyond basic functionality to include best practices, advanced features, and real-world scenarios relevant to different departments. Regular refresher sessions and updates on new features help maintain and enhance users’ proficiency. The training should be tailored to different learning styles and include both structured classroom sessions and self-paced learning options.
- Offer workshops on communication and teamwork skills
Workshops on communication and teamwork skills should be offered regularly to help employees develop the soft skills crucial for effective cross-departmental collaboration. These workshops should cover topics such as active listening, conflict resolution, giving and receiving feedback, and effective meeting facilitation. They should include practical exercises and role-playing scenarios that reflect real workplace situations, allowing participants to practice these skills in a safe environment before applying them in their daily work.
- Create mentorship programs across departments
Mentorship programs across departments need to be created to foster long-term professional relationships and knowledge transfer between different areas of the organization. These programs should carefully match mentors and mentees based on development goals and potential for mutual learning. Clear guidelines for mentorship meetings, progress tracking, and goal-setting help ensure these relationships remain productive and beneficial for both parties. Regular check-ins and support from program coordinators help maintain momentum and address any challenges that arise.
- Support professional development in complementary skills
Professional development in complementary skills must be supported to help employees build capabilities that enhance their ability to work across departmental boundaries. This might include technical skills relevant to partner departments, project management methodologies, or industry-specific knowledge. Organizations should provide resources for both formal training and informal learning opportunities, such as conferences, online courses, or professional certifications. Development plans should be aligned with both individual career goals and organizational needs for cross department expertise.
Motivate and reward collaboration
Creating incentives for collaborative behavior helps reinforce the importance of cross-departmental work:
- Implement recognition programs for successful collaborative projects
Recognition programs for successful collaborative projects should be implemented to acknowledge and celebrate teams that demonstrate exceptional cross-departmental cooperation. These programs should include both formal and informal recognition mechanisms, ranging from regular spotlight features in company communications to annual awards ceremonies. The recognition criteria should be clearly defined and transparently communicated, focusing on measurable outcomes and specific collaborative behaviors that contributed to project success. This visibility helps create a culture where collaboration is valued and actively sought out.
- Include collaboration metrics in performance reviews
Collaboration metrics must be included in performance reviews to signal its importance as a core competency and ensure it receives appropriate attention from employees at all levels. These metrics should evaluate both individual and team contributions to collaborative efforts, considering factors such as participation in cross-departmental initiatives, effectiveness in working with other departments, and specific contributions to collaborative successes. The metrics should be specific, measurable, and aligned with organizational goals while being fair and applicable across different roles and departments.
- Offer team-based bonuses for achieving shared goals
Team-based bonuses for achieving shared goals should be offered to create tangible financial incentives for effective collaboration. These bonus structures should be designed to reward collective achievement rather than individual performance, encouraging departments to work together rather than compete. The bonus criteria should be clearly defined at the outset of projects or initiatives, with regular updates on progress toward goals. The rewards should be meaningful enough to motivate real behavior change while being equitably distributed among contributing team members.
- Publicly celebrate cross-departmental successes
Public celebration of cross department successes needs to be regularly and prominently featured in organizational communications and events. This includes sharing success stories through company newsletters, intranet features, and all-hands meetings. These celebrations should go beyond simple announcements to include detailed case studies that highlight specific collaborative practices that led to success, making them learning opportunities for the entire organization. The celebrations should recognize contributions from all participating departments and individuals, reinforcing the value of diverse perspectives and skills.
- Create awards for innovative collaborative solutions
Awards for innovative collaborative solutions should be created to encourage creative approaches to cross-departmental challenges. These awards should recognize both the outcome of the collaboration and the innovative processes or approaches used to achieve it. The evaluation criteria should consider factors such as originality, effectiveness, and potential for broader application across the organization. The awards program should include opportunities for winning teams to share their approaches with others, multiplying the impact of their innovations across the organization.
Team building activities
Building personal connections across departments strengthens collaborative relationships:
- Organize cross-departmental social events
Cross-departmental social events should be organized regularly to provide opportunities for employees to interact in relaxed, informal settings outside of work pressures. These events should be thoughtfully planned to encourage mixing between departments, perhaps through themed activities or structured networking opportunities. The events should be varied in nature to appeal to different interests and personalities, ranging from casual after-work gatherings to organized outings or charitable activities. Consideration should be given to timing and accessibility to ensure maximum participation while respecting work-life balance.
- Plan team-building exercises that mix departments
Team-building exercises that mix departments need to be carefully planned to create meaningful interactions and shared experiences. These exercises should go beyond simple ice-breakers to include activities that require genuine collaboration, problem-solving, and mutual support. They should be designed to highlight different strengths and perspectives while creating opportunities for employees to discover shared interests and values. The activities should be challenging enough to be engaging but not so difficult that they create stress or anxiety among participants.
- Create mentorship programs across departments
Mentorship programs across departments should be structured to create lasting professional relationships that transcend organizational boundaries. These programs should match mentors and mentees based on development goals and potential for mutual learning, rather than just departmental needs. The relationships should be supported with clear guidelines, regular check-ins, and resources to help both parties make the most of the mentorship experience. Success stories from these relationships should be shared to inspire others and demonstrate the value of cross-departmental mentoring.
- Host informal lunch-and-learn sessions
Informal lunch-and-learn sessions should be hosted regularly to combine learning with relationship building. These sessions should feature rotating presenters from different departments sharing insights about their work, challenges, and successes. The format should encourage interactive discussion and questions, creating opportunities for genuine dialogue and understanding. Topics should be chosen to have broad appeal while offering specific insights into different aspects of the organization’s work.
- Celebrate shared successes as a unified team
Shared successes should be celebrated as a unified team to reinforce the importance of collaboration and create shared positive experiences. These celebrations should recognize contributions from all participating departments and highlight how different teams worked together to achieve results. The celebrations should be inclusive and accessible to all team members, regardless of their role or level in the organization. They should include opportunities for informal interaction and relationship building while maintaining a focus on the collective achievement being celebrated.
Optimize work processes
Streamlining workflows to support collaboration helps make it a natural part of daily operations:
- Map and analyze current cross-departmental processes
Mapping and analyzing current cross-departmental processes must be conducted thoroughly to understand existing workflows and identify areas for improvement. This analysis should include detailed documentation of how work moves between departments, including decision points, handoffs, and dependencies. Organizations should engage representatives from all involved departments to ensure accurate process mapping and gather diverse perspectives on current challenges and opportunities. This comprehensive analysis provides the foundation for meaningful process optimization.
- Identify and eliminate unnecessary steps or bottlenecks
Identifying and eliminating unnecessary steps or bottlenecks requires careful evaluation of each process component to determine its value and necessity. This evaluation should consider both the direct impact on work completion and the indirect effects on cross-departmental relationships and communication. Organizations should look for redundant approvals, unnecessary handoffs, or overly complex procedures that slow down collaboration without adding value. Special attention should be paid to points where work frequently stalls or where miscommunication often occurs.
- Standardize collaborative workflows
Standardizing collaborative workflows helps create consistency and clarity in how departments work together. These standardized processes should be documented clearly and made easily accessible to all team members. They should include well-defined roles and responsibilities, clear communication protocols, and specific guidelines for common scenarios. The standardization should be flexible enough to accommodate necessary variations while maintaining core consistency in how departments interact and work together.
- Implement automation where appropriate
Automation should be implemented thoughtfully where it can enhance collaboration without sacrificing necessary human interaction. This includes identifying repetitive tasks that can be automated, such as status updates, routine approvals, or data sharing between departments. The automation should support rather than replace meaningful human collaboration, focusing on eliminating administrative burden and reducing the potential for errors in routine tasks.
- Regularly review and update processes based on feedback
Regular review and updates of processes based on feedback ensures continuous improvement in cross-departmental collaboration. Organizations should establish systematic ways to gather feedback from all affected departments about how processes are working in practice. This feedback should be reviewed regularly, with clear mechanisms for implementing suggested improvements. The review process should also include metrics to measure the effectiveness of collaborative processes and track improvements over time.
Feedback for improvement
Establishing robust feedback mechanisms ensures continuous improvement in collaborative efforts:
- Conduct regular surveys on collaboration effectiveness
Regular surveys on collaboration effectiveness should be conducted to gather structured feedback from all participating departments. These surveys should be carefully designed to collect both quantitative and qualitative data about specific aspects of collaboration, such as communication effectiveness, process efficiency, and resource allocation. The surveys should be concise enough to encourage participation while comprehensive enough to provide actionable insights. Questions should be crafted to identify both strengths and areas for improvement in collaborative practices.
- Hold one-on-one discussions with team members
One-on-one discussions with team members need to be held regularly to gather deeper insights into collaboration challenges and opportunities. These conversations should provide a safe space for honest feedback about cross-departmental interactions, allowing employees to share concerns or suggestions they might not feel comfortable expressing in group settings. The discussions should follow a semi-structured format that ensures key topics are covered while allowing flexibility to explore emerging issues or unexpected insights.
- Implement after-action reviews for major projects
After-action reviews for major projects must be implemented to capture lessons learned and identify opportunities for improvement in collaborative processes. These reviews should be conducted promptly after project completion, while experiences are still fresh, and should include representatives from all involved departments. The reviews should examine what worked well, what could be improved, and specific recommendations for future collaborative efforts. Documentation from these reviews should be accessible to inform future project planning and process improvements.
- Create channels for ongoing feedback collection
Channels for ongoing feedback collection should be created to capture insights and suggestions as they arise, rather than waiting for scheduled review sessions. These channels should be easily accessible and user-friendly, allowing employees to submit feedback quickly and conveniently. The channels should support different types of feedback, from quick suggestions to detailed process improvement recommendations. Clear guidelines should be provided about how feedback will be reviewed and acted upon.
- Use feedback data to drive process improvements
Feedback data must be systematically used to drive process improvements in cross-departmental collaboration. Organizations should establish clear procedures for reviewing and analyzing feedback from all sources, identifying patterns and trends that indicate areas needing attention. Action plans should be developed to address significant findings, with clear ownership and timelines for implementing improvements. Regular updates should be provided to employees about how their feedback is being used to improve collaborative processes.
By implementing these strategies systematically and maintaining consistent focus on their execution, organizations can significantly improve their cross-departmental collaboration. Regular review and adjustment of these strategies ensures they remain effective and continue to meet the organization’s evolving needs.
👉 How to improve collaboration between departments? Foster open communication channels through regular meetings, shared platforms, and transparent communication protocols. Encourage cross-departmental projects and initiatives that require teams to work together towards common goals. Promote a culture of shared learning and knowledge exchange by facilitating workshops, training sessions, and mentorship programs. Establish clear roles, responsibilities, and shared objectives to ensure everyone is on the same page. Celebrate successes and recognize contributions from different departments to reinforce the value of collaboration.

Cross Departmental Collaboration Examples: Scenarios of successful cross-departmental collaboration
In this section, we’ll explore real-world examples of how different departments can work together effectively to achieve organizational goals. We’ll examine specific interactions between marketing and sales, marketing and IT, HR and IT, and sales and production departments, highlighting key collaborative processes, objectives, and outcomes. These examples demonstrate how cross-departmental collaboration can drive business success through improved efficiency, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
Working cross departmentally in marketing & sales
The collaboration between marketing and sales departments represents one of the most crucial partnerships within any organization. When these departments work together effectively, they create a powerful engine for business growth. Here are some examples of their interactions and the goals they pursue:
- Joint work on leads: Marketing generates leads through various campaigns (online advertising, content marketing, social media), and seamlessly hands them off to the sales team for qualification and follow-up. A shared CRM system is crucial for tracking leads through the sales funnel, providing both teams with visibility into the lead’s status and ensuring a smooth transition. This interaction aims to increase conversions by ensuring that qualified leads are promptly contacted and nurtured by sales.
- Creating personalized materials: Marketing leverages insights from the sales team about customer pain points, preferences, and buying behavior to develop targeted marketing materials. This could include personalized email newsletters, customized presentations, or tailored content that resonates with specific customer segments. This collaboration aligns marketing strategies with sales objectives, leading to more effective campaigns and higher conversion rates.
- Jointly developing customer offers: Marketing and sales collaborate to create compelling customer offers that address market needs and align with overall business objectives. By combining their understanding of customer preferences (marketing) and sales strategies, they can develop offers that resonate with the target audience and drive sales. This joint effort ensures that the offer is attractive, effectively communicated, and seamlessly integrated into the sales process.
These collaborative efforts between marketing and sales pursue several key goals:
- Increasing conversions: By aligning their efforts and sharing information, marketing and sales can move leads through the sales funnel more efficiently, resulting in higher conversion rates and increased revenue.
- Aligning marketing strategies with sales objectives: Collaboration ensures that marketing campaigns directly support sales goals, maximizing the return on marketing investment and driving business growth.
- Jointly developing customer offers: By working together, marketing and sales can create more compelling and effective offers that meet customer needs and drive sales performance.
Improve Team Collaboration with Virto Apps
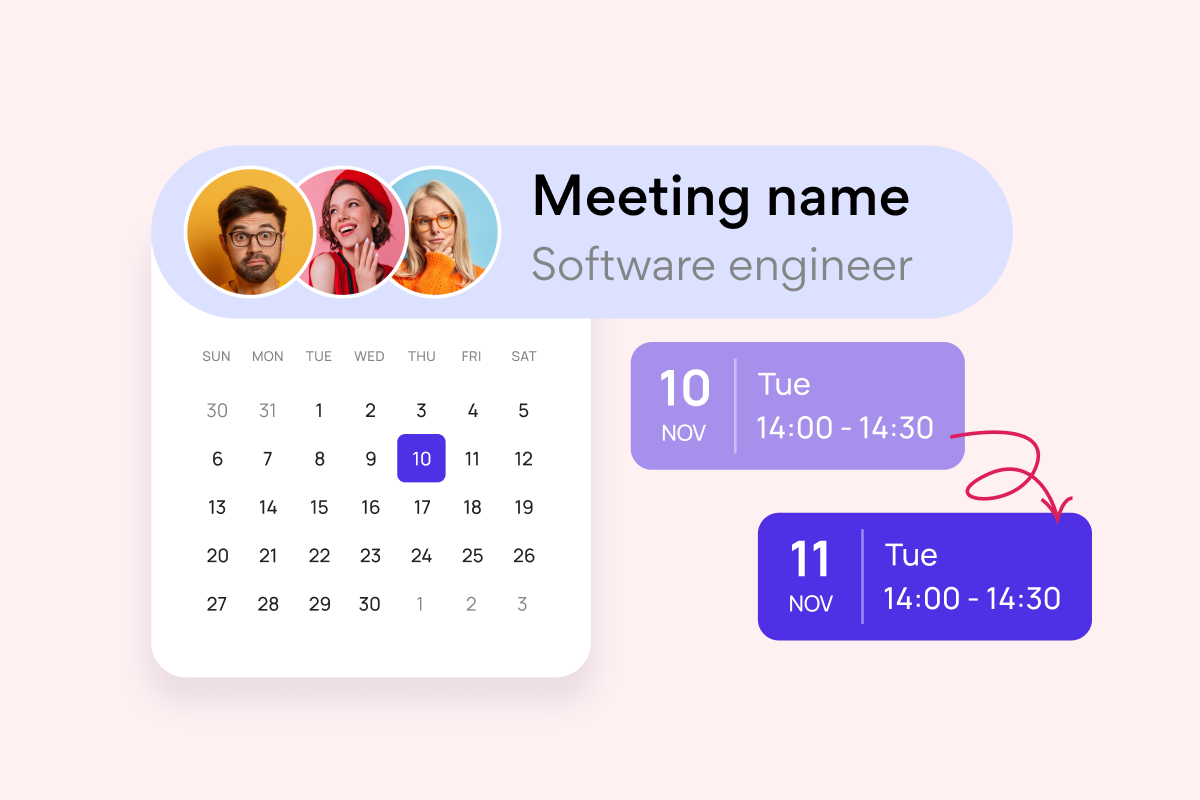
Virto Calendar
Consolidate events from SharePoint, Exchange, Google, and more into one calendar view for simplified planning.
Virto Kanban Board
This tool transforms team collaboration through visual task management for consistent stage-by-stage progress.
Virto Alerts & Reminder
Integrated within your daily tools like Microsoft Teams, the app ensures you stay ahead of all tasks and meetings.
Scenarios and examples of possible interactions between the marketing and IT departments
Effective collaboration between marketing and IT departments is essential for leveraging technology to achieve marketing objectives. Here are some examples:
- Work on the company’s website: Marketing often initiates website improvements, such as developing new landing pages or redesigning existing sections. They provide the content, structure, and desired user experience, while the IT department handles the technical implementation, ensuring the site is functional, secure, optimized for loading speed, and adaptable to different devices. This collaboration ensures that the website effectively represents the brand and provides a positive user experience.
- Optimization of analytics: The IT department implements analytics systems to track user behavior on the website and other digital platforms. Marketing then utilizes this data to understand user preferences, identify areas for improvement in online campaigns, and personalize the user experience. This data-driven approach allows marketing to optimize campaigns for better performance and improve return on investment. IT may also develop custom dashboards and reporting tools to provide marketing with readily accessible and actionable insights.
- Implementing marketing automation tools: Marketing might identify the need for marketing automation software to streamline campaigns and personalize customer interactions. IT then takes the lead in researching, selecting, and implementing the chosen platform, integrating it with existing systems, and providing training and support to the marketing team. This collaboration ensures that the chosen technology effectively meets marketing’s needs and is seamlessly integrated into the company’s IT infrastructure.
The goals of these interactions between marketing and IT include:
- Implementation of new technologies: Marketing often identifies opportunities to leverage new technologies to enhance marketing efforts. IT plays a crucial role in researching, implementing, and supporting these technologies, ensuring they are integrated effectively and securely within the existing IT infrastructure.
- Improvement of user experience: By collaborating on website development and other digital initiatives, marketing and IT can create a seamless and positive user experience across all platforms. This includes optimizing website performance, ensuring mobile responsiveness, and personalizing content based on user behavior.
- Creation and support of digital products: For companies that offer digital products or services, the collaboration between marketing and IT is essential for successful product development, launch, and ongoing support. Marketing provides insights into customer needs and market trends, while IT handles the technical development, maintenance, and security of the digital product.
Scenarios and examples of possible interactions between HR and IT departments
HR and IT departments often collaborate to streamline internal processes, improve employee experience, and leverage technology to enhance HR functions. Here are some examples:
- Onboarding: HR develops the onboarding program, which includes outlining the necessary training, paperwork, and introductions for new hires. The IT department plays a crucial role in providing new employees with the necessary access to company systems, software, and the corporate intranet or portal. This ensures a smooth and efficient onboarding experience, allowing new hires to quickly become productive members of the team. IT also often handles setting up the new employee’s workstation, configuring their email account, and providing necessary IT equipment.
- Training: IT can develop and maintain an online learning management system (LMS) for employee training. HR then utilizes this platform to deliver training courses, manage employee progress, and track completion rates. This collaboration allows HR to efficiently deliver training programs and provides employees with a convenient and accessible way to acquire new skills and knowledge. IT can also support HR by providing technical assistance with online training tools, video conferencing software for virtual training sessions, and troubleshooting any technical issues employees encounter during training.
- Performance management: HR defines the performance review process and criteria, while IT can develop or implement software to manage performance reviews, track employee goals, and provide feedback. This collaboration ensures a streamlined and efficient performance management process, allowing for better tracking of employee performance and identification of areas for improvement. IT can also support HR by ensuring the security and confidentiality of performance data.
The goals of these interactions between HR and IT include:
- Optimization of employee recruitment and onboarding processes: By working together, HR and IT can streamline these processes, reducing administrative overhead and ensuring a positive experience for new hires. This includes automating tasks, providing easy access to information, and ensuring a smooth transition into the company.
- Improvement of internal communication tools: Collaboration between HR and IT can enhance internal communication by implementing and supporting effective communication platforms. This could include intranet portals, instant messaging systems, or video conferencing tools that facilitate communication and collaboration across the organization.
- Increase in employee engagement through technology: By leveraging technology effectively, HR and IT can create a more engaging and supportive work environment. This includes providing access to learning resources, facilitating feedback mechanisms, and creating online communities that foster a sense of belonging and connection among employees.
Scenarios and examples of possible interactions between sales and production departments
Effective collaboration between sales and production is essential for meeting customer demand, optimizing inventory, and ensuring timely delivery of products or services. Here are some examples:
- Demand Forecasting: Sales gathers and analyzes market data, customer orders, and sales projections to forecast future demand. This information is shared with the production department, enabling them to adjust production schedules, manage raw material procurement, and allocate resources effectively to meet anticipated demand. Accurate demand forecasting helps prevent stockouts and minimizes overproduction.
- Problem Solving: If a customer reports a product defect or quality issue, the sales team relays this feedback to the production department. Production then investigates the issue, identifies the root cause, and implements corrective actions to prevent similar problems in the future. This collaborative approach to problem-solving ensures customer satisfaction and continuous improvement in product quality.
- Product Development: Sales teams gather valuable insights into customer needs and market trends through their direct interactions with customers. Sharing this information with the production department can inform product development decisions, ensuring that new products or features align with customer demand. This collaboration can lead to the development of more successful and market-relevant products.
- Delivery Scheduling and Coordination: Sales provides production with confirmed order details, including delivery dates and specific customer requirements. Production uses this information to schedule production runs, allocate resources, and coordinate logistics to ensure timely delivery of products to customers. Clear communication and coordination between these departments are crucial for meeting customer expectations and avoiding delivery delays.
The goals of these interactions between sales and production include:
- Optimization of Inventory Management: Accurate demand forecasting from sales allows production to optimize inventory levels, minimizing storage costs while ensuring sufficient stock to meet customer demand. This prevents both stockouts and overstocking.
- Coordination of Delivery Times with Sales Promises: Close collaboration ensures that production schedules align with delivery dates promised by the sales team, enhancing customer satisfaction and building trust.
- Improving Customer Service: By working together to address product quality issues and incorporate customer feedback into product development, sales and production contribute to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty. A seamless process for handling customer complaints and feedback builds confidence and strengthens customer relationships.
Using VirtoSoftware Apps to Simplify Collaboration
Virto Software offers tools designed to enhance cross-departmental collaboration within Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Teams environments. These apps streamline communication, scheduling, and project management, fostering greater efficiency and teamwork.
Virto Calendar App for SharePoint Online & Microsoft 365
This app provides a centralized platform for scheduling and synchronizing meetings and events across departments. Key benefits and use cases include:
- Centralized scheduling hub: Eliminates the need for multiple disparate calendars by aggregating various data sources into a single view. Teams can easily see each other’s availability, preventing scheduling conflicts and improving coordination.
- Diverse data source integration: Integrates with SharePoint lists, Outlook calendars, Microsoft Planner, Google Calendar, and other iCal feeds, providing a comprehensive overview of all relevant events and deadlines.
- Cross-departmental project management: Facilitates project planning by allowing teams to visualize project milestones, deadlines, and individual responsibilities on a shared calendar. This improves transparency and accountability across departments.
- Use case: A marketing team launching a new product can use the Virto Calendar to coordinate tasks with the sales, product development, and IT departments. The calendar can track deadlines for marketing materials, sales training, product development milestones, and IT infrastructure setup, ensuring everyone is aligned and working towards the common goal.
Virto Calendar App for Microsoft Teams
This app brings the power of Virto Calendar directly into the Microsoft Teams environment, further simplifying collaboration and communication. Key benefits and use cases include:
- Streamlined communication: Integrates seamlessly with Microsoft Teams, allowing users to schedule meetings, view team availability, and manage events directly within their existing workflow.
- Enhanced team coordination: Provides a shared view of team schedules, facilitating better coordination of meetings, project tasks, and deadlines.
- Simplified remote work: Helps distributed teams stay connected and organized by providing a central platform for scheduling and communication, regardless of location.
- Use case: A sales team can use the Virto Calendar app within Microsoft Teams to coordinate client meetings, track sales calls, and manage their individual schedules. This ensures everyone is aware of client interactions and avoids scheduling conflicts.
Key benefits of using Virto Calendar Apps
- Improved communication: Centralized calendars and integrated communication tools enhance transparency and reduce misunderstandings.
- Increased efficiency: Streamlined scheduling and task management free up time and resources, allowing teams to focus on their core responsibilities.
- Enhanced collaboration: Shared calendars and project timelines foster a sense of teamwork and improve coordination across departments.
- Better project management: Visualizing project milestones and deadlines on a shared calendar improves project tracking and accountability.
By leveraging the features of Virto Calendar apps, organizations can significantly improve cross-departmental collaboration, leading to increased productivity, better project outcomes, and a more cohesive work environment.
👉 Want to learn more about VirtoSoftware apps in different scenarios and industries? Then check out our dedicated use case pages:
- VirtoSoftware Main Use Case Page
- Cross-Departmental Event Coordination
- Client Appointment Scheduling
- Remote Team Collaboration
- Resource Booking System
- Agile Project Management
Conclusion on Working Across Different Departments
Throughout this article, we’ve explored how effective collaboration between departments drives innovation, improves efficiency, and creates a more cohesive organizational culture. The benefits are clear: enhanced communication, increased productivity, improved employee satisfaction, and better customer service outcomes.
The key to successful crossdepartmental collaboration lies in implementing the right combination of strategies, processes, and tools. From establishing clear goals and responsibilities to creating effective feedback mechanisms, organizations must take a systematic approach to breaking down silos and fostering cooperation between departments.
Modern solutions like the Virto Calendar App for SharePoint Online & Microsoft 365 and Virto Calendar App for Microsoft Teams play a crucial role in facilitating this collaboration. These tools provide the technical infrastructure needed to coordinate activities, schedule meetings, and manage resources effectively across departments. By centralizing calendar management and providing comprehensive integration capabilities, they help teams work together more efficiently and achieve their shared objectives. We encourage you to check out these tools yourself by scheduling a quick demo or installing free trial versions of the apps:
For more insights on improving team collaboration and calendar management, we invite you to explore additional resources on our blog: